Class Layout
- All Implemented Interfaces:
Proxy
PangoLayout structure represents an entire paragraph of text.
While complete access to the layout capabilities of Pango is provided
using the detailed interfaces for itemization and shaping, using
that functionality directly involves writing a fairly large amount
of code. PangoLayout provides a high-level driver for formatting
entire paragraphs of text at once. This includes paragraph-level
functionality such as line breaking, justification, alignment and
ellipsization.
A PangoLayout is initialized with a PangoContext, UTF-8 string
and set of attributes for that string. Once that is done, the set of
formatted lines can be extracted from the object, the layout can be
rendered, and conversion between logical character positions within
the layout's text, and the physical position of the resulting glyphs
can be made.
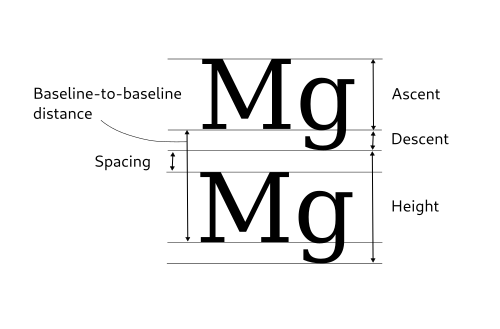
There are a number of parameters to adjust the formatting of a
PangoLayout. The following image shows adjustable parameters
(on the left) and font metrics (on the right):
The following images demonstrate the effect of alignment and justification on the layout of text:
| | |
| --- | --- |
|  |
|  |
|
|
|  |
|  |
|
|
|  |
|  |
|
It is possible, as well, to ignore the 2-D setup,
and simply treat the results of a PangoLayout as a list of lines.
-
Nested Class Summary
Nested ClassesModifier and TypeClassDescriptionstatic classLayout.Builder<B extends Layout.Builder<B>>Inner class implementing a builder pattern to construct a GObject with properties.static classNested classes/interfaces inherited from class org.gnome.gobject.GObject
GObject.NotifyCallback, GObject.ObjectClass -
Constructor Summary
ConstructorsConstructorDescriptionLayout()Creates a new Layout.Layout(MemorySegment address) Create a Layout proxy instance for the provided memory address.Create a newPangoLayoutobject with attributes initialized to default values for a particularPangoContext. -
Method Summary
Modifier and TypeMethodDescriptionprotected LayoutasParent()Returns this instance as if it were its parent type.static Layout.Builder<? extends Layout.Builder> builder()ALayout.Builderobject constructs aLayoutwith the specified properties.voidForces recomputation of any state in thePangoLayoutthat might depend on the layout's context.copy()Creates a deep copy-by-value of the layout.static @Nullable Layoutdeserialize(Context context, byte[] bytes, Set<LayoutDeserializeFlags> flags) Loads data previously created viaserialize(java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutSerializeFlags>).static @Nullable Layoutdeserialize(Context context, byte[] bytes, LayoutDeserializeFlags... flags) Loads data previously created viaserialize(java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutSerializeFlags>).Gets the alignment for the layout: how partial lines are positioned within the horizontal space available.@Nullable AttrListGets the attribute list for the layout, if any.booleanGets whether to calculate the base direction for the layout according to its contents.intGets the Y position of baseline of the first line inlayout.voidgetCaretPos(int index, @Nullable Rectangle strongPos, @Nullable Rectangle weakPos) Given an index within a layout, determines the positions that of the strong and weak cursors if the insertion point is at that index.intReturns the number of Unicode characters in the the text oflayout.Retrieves thePangoContextused for this layout.voidgetCursorPos(int index, @Nullable Rectangle strongPos, @Nullable Rectangle weakPos) Given an index within a layout, determines the positions that of the strong and weak cursors if the insertion point is at that index.getDirection(int index) Gets the text direction at the given character position inlayout.Gets the type of ellipsization being performed forlayout.voidgetExtents(@Nullable Rectangle inkRect, @Nullable Rectangle logicalRect) Computes the logical and ink extents oflayout.@Nullable FontDescriptionGets the font description for the layout, if any.intGets the height of layout used for ellipsization.intGets the paragraph indent width in Pango units.getIter()Returns an iterator to iterate over the visual extents of the layout.booleanGets whether each complete line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.booleanGets whether the last line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.@Nullable LayoutLinegetLine(int line) Retrieves a particular line from aPangoLayout.intRetrieves the count of lines for thelayout.@Nullable LayoutLinegetLineReadonly(int line) Retrieves a particular line from aPangoLayout.getLines()Returns the lines of the this Layout as a list.floatGets the line spacing factor oflayout.Returns the lines of the this Layout as a list.voidgetLogAttrs(@Nullable Out<LogAttr[]> attrs) Retrieves an array of logical attributes for each character in thelayout.LogAttr[]Retrieves an array of logical attributes for each character in thelayout.static MemoryLayoutThe memory layout of the native struct.voidgetPixelExtents(@Nullable Rectangle inkRect, @Nullable Rectangle logicalRect) Computes the logical and ink extents of this Layout in device units.voidgetPixelSize(@Nullable Out<Integer> width, @Nullable Out<Integer> height) Determines the logical width and height of aPangoLayoutin device units.intReturns the current serial number oflayout.booleanObtains whether this Layout is in single paragraph mode.voidDetermines the logical width and height of aPangoLayoutin Pango units.intGets the amount of spacing between the lines of the layout.@Nullable TabArraygetTabs()Gets the currentPangoTabArrayused by this layout.getText()Gets the text in the layout.static @Nullable TypegetType()Get the GType of the Layout classintCounts the number of unknown glyphs inlayout.intgetWidth()Gets the width to which the lines of thePangoLayoutshould wrap.getWrap()Gets the wrap mode for the layout.voidindexToLineX(int index, boolean trailing, @Nullable Out<Integer> line, @Nullable Out<Integer> xPos) Converts from byteindexwithin the this Layout to line and X position.voidindexToPos(int index, Rectangle pos) Converts from an index within aPangoLayoutto the onscreen position corresponding to the grapheme at that index.booleanQueries whether the layout had to ellipsize any paragraphs.booleanQueries whether the layout had to wrap any paragraphs.voidmoveCursorVisually(boolean strong, int oldIndex, int oldTrailing, int direction, Out<Integer> newIndex, Out<Integer> newTrailing) Computes a new cursor position from an old position and a direction.byte[]serialize(Set<LayoutSerializeFlags> flags) Serializes the this Layout for later deserialization viadeserialize(org.gnome.pango.Context, byte[], java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutDeserializeFlags>).byte[]serialize(LayoutSerializeFlags... flags) Serializes the this Layout for later deserialization viadeserialize(org.gnome.pango.Context, byte[], java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutDeserializeFlags>).voidsetAlignment(Alignment alignment) Sets the alignment for the layout: how partial lines are positioned within the horizontal space available.voidsetAttributes(@Nullable AttrList attrs) Sets the text attributes for a layout object.voidsetAutoDir(boolean autoDir) Sets whether to calculate the base direction for the layout according to its contents.voidsetEllipsize(EllipsizeMode ellipsize) Sets the type of ellipsization being performed forlayout.voidsetFontDescription(@Nullable FontDescription desc) Sets the default font description for the layout.voidsetHeight(int height) Sets the height to which thePangoLayoutshould be ellipsized at.voidsetIndent(int indent) Sets the width in Pango units to indent each paragraph.voidsetJustify(boolean justify) Sets whether each complete line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.voidsetJustifyLastLine(boolean justify) Sets whether the last line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.voidsetLineSpacing(float factor) Sets a factor for line spacing.voidSets the layout text and attribute list from marked-up text.voidsetMarkupWithAccel(String markup, int length, int accelMarker, @Nullable Out<Integer> accelChar) Sets the layout text and attribute list from marked-up text.voidsetSingleParagraphMode(boolean setting) Sets the single paragraph mode oflayout.voidsetSpacing(int spacing) Sets the amount of spacing in Pango units between the lines of the layout.voidSets the tabs to use forlayout,overriding the default tabs.voidSets the text of the layout.voidsetWidth(int width) Sets the width to which the lines of thePangoLayoutshould wrap or get ellipsized.voidSets the wrap mode.booleanwriteToFile(Set<LayoutSerializeFlags> flags, String filename) A convenience method to serialize a layout to a file.booleanwriteToFile(LayoutSerializeFlags flags, String filename) A convenience method to serialize a layout to a file.booleanConverts from X and Y position within a layout to the byte index to the character at that logical position.Methods inherited from class org.gnome.gobject.GObject
addToggleRef, addWeakPointer, bindProperty, bindProperty, bindProperty, bindPropertyFull, bindPropertyFull, bindPropertyWithClosures, bindPropertyWithClosures, compatControl, connect, connect, connect, constructed, disconnect, dispatchPropertiesChanged, dispose, dupData, dupQdata, emit, emitNotify, finalize_, forceFloating, freezeNotify, get, getData, getProperty, getProperty, getProperty, getQdata, getv, interfaceFindProperty, interfaceInstallProperty, interfaceListProperties, isFloating, newInstance, newInstance, newv, notify, notify, notifyByPspec, onNotify, ref, refSink, removeToggleRef, removeWeakPointer, replaceData, replaceQdata, runDispose, set, setData, setDataFull, setProperty, setProperty, setProperty, setQdata, setQdataFull, setv, stealData, stealQdata, takeRef, thawNotify, unref, watchClosure, weakRef, weakUnref, withPropertiesMethods inherited from class org.gnome.gobject.TypeInstance
callParent, callParent, cast, getPrivate, readGClass, writeGClassMethods inherited from class org.javagi.base.ProxyInstance
equals, handle, hashCode
-
Constructor Details
-
Layout
Create a Layout proxy instance for the provided memory address.- Parameters:
address- the memory address of the native object
-
Layout
Create a newPangoLayoutobject with attributes initialized to default values for a particularPangoContext.- Parameters:
context- aPangoContext
-
Layout
public Layout()Creates a new Layout.
-
-
Method Details
-
getType
-
getMemoryLayout
The memory layout of the native struct.- Returns:
- the memory layout
-
asParent
Returns this instance as if it were its parent type. This is mostly synonymous to the Javasuperkeyword, but will set the native typeclass function pointers to the parent type. When overriding a native virtual method in Java, "chaining up" withsuper.methodName()doesn't work, because it invokes the overridden function pointer again. To chain up, callasParent().methodName(). This will call the native function pointer of this virtual method in the typeclass of the parent type. -
deserialize
public static @Nullable Layout deserialize(Context context, byte[] bytes, Set<LayoutDeserializeFlags> flags) throws GErrorException Loads data previously created viaserialize(java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutSerializeFlags>).For a discussion of the supported format, see that function.
Note: to verify that the returned layout is identical to the one that was serialized, you can compare
bytesto the result of serializing the layout again.- Parameters:
context- aPangoContextbytes- the bytes containing the dataflags-PangoLayoutDeserializeFlags- Returns:
- a new
PangoLayout - Throws:
GErrorException- seeGError- Since:
- 1.50
-
deserialize
public static @Nullable Layout deserialize(Context context, byte[] bytes, LayoutDeserializeFlags... flags) throws GErrorException Loads data previously created viaserialize(java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutSerializeFlags>).For a discussion of the supported format, see that function.
Note: to verify that the returned layout is identical to the one that was serialized, you can compare
bytesto the result of serializing the layout again.- Parameters:
context- aPangoContextbytes- the bytes containing the dataflags-PangoLayoutDeserializeFlags- Returns:
- a new
PangoLayout - Throws:
GErrorException- seeGError- Since:
- 1.50
-
contextChanged
public void contextChanged()Forces recomputation of any state in thePangoLayoutthat might depend on the layout's context.This function should be called if you make changes to the context subsequent to creating the layout.
-
copy
Creates a deep copy-by-value of the layout.The attribute list, tab array, and text from the original layout are all copied by value.
- Returns:
- the newly allocated
PangoLayout
-
getAlignment
Gets the alignment for the layout: how partial lines are positioned within the horizontal space available.- Returns:
- the alignment
-
getAttributes
Gets the attribute list for the layout, if any.- Returns:
- a
PangoAttrList
-
getAutoDir
public boolean getAutoDir()Gets whether to calculate the base direction for the layout according to its contents.See
setAutoDir(boolean).- Returns:
trueif the bidirectional base direction is computed from the layout's contents,falseotherwise- Since:
- 1.4
-
getBaseline
public int getBaseline()Gets the Y position of baseline of the first line inlayout.- Returns:
- baseline of first line, from top of this Layout
- Since:
- 1.22
-
getCaretPos
Given an index within a layout, determines the positions that of the strong and weak cursors if the insertion point is at that index.This is a variant of
getCursorPos(int, org.gnome.pango.Rectangle, org.gnome.pango.Rectangle)that applies font metric information about caret slope and offset to the positions it returns.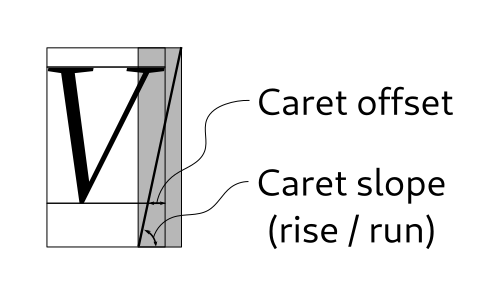
- Parameters:
index- the byte index of the cursorstrongPos- location to store the strong cursor positionweakPos- location to store the weak cursor position- Since:
- 1.50
-
getCharacterCount
public int getCharacterCount()Returns the number of Unicode characters in the the text oflayout.- Returns:
- the number of Unicode characters in the text of this Layout
- Since:
- 1.30
-
getContext
Retrieves thePangoContextused for this layout.- Returns:
- the
PangoContextfor the layout
-
getCursorPos
Given an index within a layout, determines the positions that of the strong and weak cursors if the insertion point is at that index.The position of each cursor is stored as a zero-width rectangle with the height of the run extents.
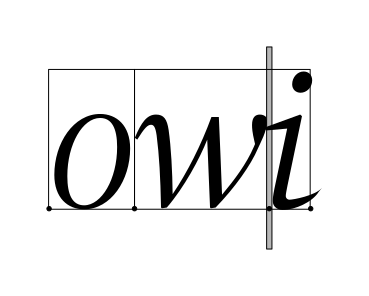
The strong cursor location is the location where characters of the directionality equal to the base direction of the layout are inserted. The weak cursor location is the location where characters of the directionality opposite to the base direction of the layout are inserted.
The following example shows text with both a strong and a weak cursor.
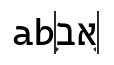
The strong cursor has a little arrow pointing to the right, the weak cursor to the left. Typing a 'c' in this situation will insert the character after the 'b', and typing another Hebrew character, like 'ג', will insert it at the end.
- Parameters:
index- the byte index of the cursorstrongPos- location to store the strong cursor positionweakPos- location to store the weak cursor position
-
getDirection
Gets the text direction at the given character position inlayout.- Parameters:
index- the byte index of the char- Returns:
- the text direction at
index - Since:
- 1.46
-
getEllipsize
Gets the type of ellipsization being performed forlayout.See
setEllipsize(org.gnome.pango.EllipsizeMode).Use
isEllipsized()to query whether any paragraphs were actually ellipsized.- Returns:
- the current ellipsization mode for this Layout
- Since:
- 1.6
-
getExtents
Computes the logical and ink extents oflayout.Logical extents are usually what you want for positioning things. Note that both extents may have non-zero x and y. You may want to use those to offset where you render the layout. Not doing that is a very typical bug that shows up as right-to-left layouts not being correctly positioned in a layout with a set width.
The extents are given in layout coordinates and in Pango units; layout coordinates begin at the top left corner of the layout.
- Parameters:
inkRect- rectangle used to store the extents of the layout as drawnlogicalRect- rectangle used to store the logical extents of the layout
-
getFontDescription
Gets the font description for the layout, if any.- Returns:
- a pointer to the
layout's font description, or
nullif the font description from the layout's context is inherited. - Since:
- 1.8
-
getHeight
public int getHeight()Gets the height of layout used for ellipsization.See
setHeight(int)for details.- Returns:
- the height, in Pango units if positive, or number of lines if negative.
- Since:
- 1.20
-
getIndent
public int getIndent()Gets the paragraph indent width in Pango units.A negative value indicates a hanging indentation.
- Returns:
- the indent in Pango units
-
getIter
Returns an iterator to iterate over the visual extents of the layout.- Returns:
- the new
PangoLayoutIter
-
getJustify
public boolean getJustify()Gets whether each complete line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.- Returns:
- the justify value
-
getJustifyLastLine
public boolean getJustifyLastLine()Gets whether the last line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.- Returns:
- the justify value
- Since:
- 1.50
-
getLine
Retrieves a particular line from aPangoLayout.Use the faster
getLineReadonly(int)if you do not plan to modify the contents of the line (glyphs, glyph widths, etc.).- Parameters:
line- the index of a line, which must be between 0 andpango_layout_get_line_count(layout) - 1, inclusive.- Returns:
- the requested
PangoLayoutLine, ornullif the index is out of range. This layout line can be ref'ed and retained, but will become invalid if changes are made to thePangoLayout.
-
getLineCount
public int getLineCount()Retrieves the count of lines for thelayout.- Returns:
- the line count
-
getLineReadonly
Retrieves a particular line from aPangoLayout.This is a faster alternative to
getLine(int), but the user is not expected to modify the contents of the line (glyphs, glyph widths, etc.).- Parameters:
line- the index of a line, which must be between 0 andpango_layout_get_line_count(layout) - 1, inclusive.- Returns:
- the requested
PangoLayoutLine, ornullif the index is out of range. This layout line can be ref'ed and retained, but will become invalid if changes are made to thePangoLayout. No changes should be made to the line. - Since:
- 1.16
-
getLineSpacing
public float getLineSpacing()Gets the line spacing factor oflayout.- Since:
- 1.44
-
getLines
Returns the lines of the this Layout as a list.Use the faster
getLinesReadonly()if you do not plan to modify the contents of the lines (glyphs, glyph widths, etc.).- Returns:
- a
GSListcontaining the lines in the layout. This points to internal data of thePangoLayoutand must be used with care. It will become invalid on any change to the layout's text or properties.
-
getLinesReadonly
Returns the lines of the this Layout as a list.This is a faster alternative to
getLines(), but the user is not expected to modify the contents of the lines (glyphs, glyph widths, etc.).- Returns:
- a
GSListcontaining the lines in the layout. This points to internal data of thePangoLayoutand must be used with care. It will become invalid on any change to the layout's text or properties. No changes should be made to the lines. - Since:
- 1.16
-
getLogAttrs
-
getLogAttrsReadonly
Retrieves an array of logical attributes for each character in thelayout.This is a faster alternative to
getLogAttrs(org.javagi.base.Out<org.gnome.pango.LogAttr[]>). The returned array is part of this Layout and must not be modified. Modifying the layout will invalidate the returned array.The number of attributes returned in
nAttrswill be one more than the total number of characters in the layout, since there need to be attributes corresponding to both the position before the first character and the position after the last character.- Returns:
- an array of logical attributes
- Since:
- 1.30
-
getPixelExtents
Computes the logical and ink extents of this Layout in device units.This function just calls
getExtents(org.gnome.pango.Rectangle, org.gnome.pango.Rectangle)followed by twoPango.extentsToPixels(org.gnome.pango.Rectangle, org.gnome.pango.Rectangle)calls, roundinginkRectandlogicalRectsuch that the rounded rectangles fully contain the unrounded one (that is, passes them as first argument toPango.extentsToPixels(org.gnome.pango.Rectangle, org.gnome.pango.Rectangle)).- Parameters:
inkRect- rectangle used to store the extents of the layout as drawnlogicalRect- rectangle used to store the logical extents of the layout
-
getPixelSize
Determines the logical width and height of aPangoLayoutin device units.getSize(org.javagi.base.Out<java.lang.Integer>, org.javagi.base.Out<java.lang.Integer>)returns the width and height scaled byPANGO_SCALE. This is simply a convenience function aroundgetPixelExtents(org.gnome.pango.Rectangle, org.gnome.pango.Rectangle).- Parameters:
width- location to store the logical widthheight- location to store the logical height
-
getSerial
public int getSerial()Returns the current serial number oflayout.The serial number is initialized to an small number larger than zero when a new layout is created and is increased whenever the layout is changed using any of the setter functions, or the
PangoContextit uses has changed. The serial may wrap, but will never have the value 0. Since it can wrap, never compare it with "less than", always use "not equals".This can be used to automatically detect changes to a
PangoLayout, and is useful for example to decide whether a layout needs redrawing. To force the serial to be increased, usecontextChanged().- Returns:
- The current serial number of
layout. - Since:
- 1.32.4
-
getSingleParagraphMode
public boolean getSingleParagraphMode()Obtains whether this Layout is in single paragraph mode.- Returns:
trueif the layout does not break paragraphs at paragraph separator characters,falseotherwise
-
getSize
Determines the logical width and height of aPangoLayoutin Pango units.This is simply a convenience function around
getExtents(org.gnome.pango.Rectangle, org.gnome.pango.Rectangle).- Parameters:
width- location to store the logical widthheight- location to store the logical height
-
getSpacing
public int getSpacing()Gets the amount of spacing between the lines of the layout.- Returns:
- the spacing in Pango units
-
getTabs
Gets the currentPangoTabArrayused by this layout.If no
PangoTabArrayhas been set, then the default tabs are in use andnullis returned. Default tabs are every 8 spaces.The return value should be freed with
TabArray.free().- Returns:
- a copy of the tabs for this layout
-
getText
Gets the text in the layout.The returned text should not be freed or modified.
- Returns:
- the text in the this Layout
-
getUnknownGlyphsCount
public int getUnknownGlyphsCount()Counts the number of unknown glyphs inlayout.This function can be used to determine if there are any fonts available to render all characters in a certain string, or when used in combination with
AttrType.FALLBACK, to check if a certain font supports all the characters in the string.- Returns:
- The number of unknown glyphs in this Layout
- Since:
- 1.16
-
getWidth
public int getWidth()Gets the width to which the lines of thePangoLayoutshould wrap.- Returns:
- the width in Pango units, or -1 if no width set.
-
getWrap
Gets the wrap mode for the layout.Use
isWrapped()to query whether any paragraphs were actually wrapped.- Returns:
- active wrap mode.
-
indexToLineX
public void indexToLineX(int index, boolean trailing, @Nullable Out<Integer> line, @Nullable Out<Integer> xPos) Converts from byteindexwithin the this Layout to line and X position.The X position is measured from the left edge of the line.
- Parameters:
index- the byte index of a grapheme within the layouttrailing- an integer indicating the edge of the grapheme to retrieve the position of. If > 0, the trailing edge of the grapheme, if 0, the leading of the graphemeline- location to store resulting line index. (which will between 0 and pango_layout_get_line_count(layout) - 1)xPos- location to store resulting position within line (PANGO_SCALEunits per device unit)
-
indexToPos
Converts from an index within aPangoLayoutto the onscreen position corresponding to the grapheme at that index.The returns is represented as rectangle. Note that
pos->xis always the leading edge of the grapheme andpos->x + pos->widththe trailing edge of the grapheme. If the directionality of the grapheme is right-to-left, thenpos->widthwill be negative.- Parameters:
index- byte index within this Layoutpos- rectangle in which to store the position of the grapheme
-
isEllipsized
public boolean isEllipsized()Queries whether the layout had to ellipsize any paragraphs.This returns
trueif the ellipsization mode for this Layout is notEllipsizeMode.NONE, a positive width is set onlayout,and there are paragraphs exceeding that width that have to be ellipsized.- Returns:
trueif any paragraphs had to be ellipsized,falseotherwise- Since:
- 1.16
-
isWrapped
public boolean isWrapped()Queries whether the layout had to wrap any paragraphs.This returns
trueif a positive width is set onlayout,and there are paragraphs exceeding the layout width that have to be wrapped.- Returns:
trueif any paragraphs had to be wrapped,falseotherwise- Since:
- 1.16
-
moveCursorVisually
public void moveCursorVisually(boolean strong, int oldIndex, int oldTrailing, int direction, Out<Integer> newIndex, Out<Integer> newTrailing) Computes a new cursor position from an old position and a direction.If
directionis positive, then the new position will cause the strong or weak cursor to be displayed one position to right of where it was with the old cursor position. Ifdirectionis negative, it will be moved to the left.In the presence of bidirectional text, the correspondence between logical and visual order will depend on the direction of the current run, and there may be jumps when the cursor is moved off of the end of a run.
Motion here is in cursor positions, not in characters, so a single call to this function may move the cursor over multiple characters when multiple characters combine to form a single grapheme.
- Parameters:
strong- whether the moving cursor is the strong cursor or the weak cursor. The strong cursor is the cursor corresponding to text insertion in the base direction for the layout.oldIndex- the byte index of the current cursor positionoldTrailing- if 0, the cursor was at the leading edge of the grapheme indicated byoldIndex,if > 0, the cursor was at the trailing edge.direction- direction to move cursor. A negative value indicates motion to the leftnewIndex- location to store the new cursor byte index. A value of -1 indicates that the cursor has been moved off the beginning of the layout. A value ofG_MAXINTindicates that the cursor has been moved off the end of the layout.newTrailing- number of characters to move forward from the location returned fornewIndexto get the position where the cursor should be displayed. This allows distinguishing the position at the beginning of one line from the position at the end of the preceding line.newIndexis always on the line where the cursor should be displayed.
-
serialize
Serializes the this Layout for later deserialization viadeserialize(org.gnome.pango.Context, byte[], java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutDeserializeFlags>).There are no guarantees about the format of the output across different versions of Pango and
deserialize(org.gnome.pango.Context, byte[], java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutDeserializeFlags>)will reject data that it cannot parse.The intended use of this function is testing, benchmarking and debugging. The format is not meant as a permanent storage format.
- Parameters:
flags-PangoLayoutSerializeFlags- Returns:
- a
GBytescontaining the serialized form of this Layout - Since:
- 1.50
-
serialize
Serializes the this Layout for later deserialization viadeserialize(org.gnome.pango.Context, byte[], java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutDeserializeFlags>).There are no guarantees about the format of the output across different versions of Pango and
deserialize(org.gnome.pango.Context, byte[], java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutDeserializeFlags>)will reject data that it cannot parse.The intended use of this function is testing, benchmarking and debugging. The format is not meant as a permanent storage format.
- Parameters:
flags-PangoLayoutSerializeFlags- Returns:
- a
GBytescontaining the serialized form of this Layout - Since:
- 1.50
-
setAlignment
Sets the alignment for the layout: how partial lines are positioned within the horizontal space available.The default alignment is
Alignment.LEFT.- Parameters:
alignment- the alignment
-
setAttributes
Sets the text attributes for a layout object.References
attrs,so the caller can unref its reference.- Parameters:
attrs- aPangoAttrList
-
setAutoDir
public void setAutoDir(boolean autoDir) Sets whether to calculate the base direction for the layout according to its contents.When this flag is on (the default), then paragraphs in this Layout that begin with strong right-to-left characters (Arabic and Hebrew principally), will have right-to-left layout, paragraphs with letters from other scripts will have left-to-right layout. Paragraphs with only neutral characters get their direction from the surrounding paragraphs.
When
false, the choice between left-to-right and right-to-left layout is done according to the base direction of the layout'sPangoContext. (SeeContext.setBaseDir(org.gnome.pango.Direction)).When the auto-computed direction of a paragraph differs from the base direction of the context, the interpretation of
Alignment.LEFTandAlignment.RIGHTare swapped.- Parameters:
autoDir- iftrue, compute the bidirectional base direction from the layout's contents- Since:
- 1.4
-
setEllipsize
Sets the type of ellipsization being performed forlayout.Depending on the ellipsization mode
ellipsizetext is removed from the start, middle, or end of text so they fit within the width and height of layout set withsetWidth(int)andsetHeight(int).If the layout contains characters such as newlines that force it to be layed out in multiple paragraphs, then whether each paragraph is ellipsized separately or the entire layout is ellipsized as a whole depends on the set height of the layout.
The default value is
EllipsizeMode.NONE.See
setHeight(int)for details.- Parameters:
ellipsize- the new ellipsization mode for this Layout- Since:
- 1.6
-
setFontDescription
Sets the default font description for the layout.If no font description is set on the layout, the font description from the layout's context is used.
- Parameters:
desc- the newPangoFontDescriptionto unset the current font description
-
setHeight
public void setHeight(int height) Sets the height to which thePangoLayoutshould be ellipsized at.There are two different behaviors, based on whether
heightis positive or negative.If
heightis positive, it will be the maximum height of the layout. Only lines would be shown that would fit, and if there is any text omitted, an ellipsis added. At least one line is included in each paragraph regardless of how small the height value is. A value of zero will render exactly one line for the entire layout.If
heightis negative, it will be the (negative of) maximum number of lines per paragraph. That is, the total number of lines shown may well be more than this value if the layout contains multiple paragraphs of text. The default value of -1 means that the first line of each paragraph is ellipsized. This behavior may be changed in the future to act per layout instead of per paragraph. File a bug against pango at https://gitlab.gnome.org/gnome/pango if your code relies on this behavior.Height setting only has effect if a positive width is set on this Layout and ellipsization mode of this Layout is not
EllipsizeMode.NONE. The behavior is undefined if a height other than -1 is set and ellipsization mode is set toEllipsizeMode.NONE, and may change in the future.- Parameters:
height- the desired height of the layout in Pango units if positive, or desired number of lines if negative.- Since:
- 1.20
-
setIndent
public void setIndent(int indent) Sets the width in Pango units to indent each paragraph.A negative value of
indentwill produce a hanging indentation. That is, the first line will have the full width, and subsequent lines will be indented by the absolute value ofindent.The indent setting is ignored if layout alignment is set to
Alignment.CENTER.The default value is 0.
- Parameters:
indent- the amount by which to indent
-
setJustify
public void setJustify(boolean justify) Sets whether each complete line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.Stretching is typically done by adding whitespace, but for some scripts (such as Arabic), the justification may be done in more complex ways, like extending the characters.
Note that this setting is not implemented and so is ignored in Pango older than 1.18.
Note that tabs and justification conflict with each other: Justification will move content away from its tab-aligned positions.
The default value is
false.Also see
setJustifyLastLine(boolean).- Parameters:
justify- whether the lines in the layout should be justified
-
setJustifyLastLine
public void setJustifyLastLine(boolean justify) Sets whether the last line should be stretched to fill the entire width of the layout.This only has an effect if
setJustify(boolean)has been called as well.The default value is
false.- Parameters:
justify- whether the last line in the layout should be justified- Since:
- 1.50
-
setLineSpacing
public void setLineSpacing(float factor) Sets a factor for line spacing.Typical values are: 0, 1, 1.5, 2. The default values is 0.
If
factoris non-zero, lines are placed so thatbaseline2 = baseline1 + factor * height2
where height2 is the line height of the second line (as determined by the font(s)). In this case, the spacing set with
setSpacing(int)is ignored.If
factoris zero (the default), spacing is applied as before.Note: for semantics that are closer to the CSS line-height property, see
Pango.attrLineHeightNew(double).- Parameters:
factor- the new line spacing factor- Since:
- 1.44
-
setMarkup
Sets the layout text and attribute list from marked-up text.See Pango Markup).
Replaces the current text and attribute list.
This is the same as
setMarkupWithAccel(java.lang.String, int, int, org.javagi.base.Out<java.lang.Integer>), but the markup text isn't scanned for accelerators.- Parameters:
markup- marked-up textlength- length of marked-up text in bytes, or -1 ifmarkupisNUL-terminated
-
setMarkupWithAccel
public void setMarkupWithAccel(String markup, int length, int accelMarker, @Nullable Out<Integer> accelChar) Sets the layout text and attribute list from marked-up text.See Pango Markup).
Replaces the current text and attribute list.
If
accelMarkeris nonzero, the given character will mark the character following it as an accelerator. For example,accelMarkermight be an ampersand or underscore. All characters marked as an accelerator will receive aUnderline.LOWattribute, and the first character so marked will be returned inaccelChar.TwoaccelMarkercharacters following each other produce a single literalaccelMarkercharacter.- Parameters:
markup- marked-up text (see Pango Markup)length- length of marked-up text in bytes, or -1 ifmarkupisNUL-terminatedaccelMarker- marker for accelerators in the textaccelChar- return location for first located accelerator
-
setSingleParagraphMode
public void setSingleParagraphMode(boolean setting) Sets the single paragraph mode oflayout.If
settingistrue, do not treat newlines and similar characters as paragraph separators; instead, keep all text in a single paragraph, and display a glyph for paragraph separator characters. Used when you want to allow editing of newlines on a single text line.The default value is
false.- Parameters:
setting- new setting
-
setSpacing
public void setSpacing(int spacing) Sets the amount of spacing in Pango units between the lines of the layout.When placing lines with spacing, Pango arranges things so that
line2.top = line1.bottom + spacing
The default value is 0.
Note: Since 1.44, Pango is using the line height (as determined by the font) for placing lines when the line spacing factor is set to a non-zero value with
setLineSpacing(float). In that case, thespacingset with this function is ignored.Note: for semantics that are closer to the CSS line-height property, see
Pango.attrLineHeightNew(double).- Parameters:
spacing- the amount of spacing
-
setTabs
Sets the tabs to use forlayout,overriding the default tabs.PangoLayoutwill place content at the next tab position whenever it meets a Tab character (U+0009).By default, tabs are every 8 spaces. If
tabsisnull, the default tabs are reinstated.tabsis copied into the layout; you must free your copy oftabsyourself.Note that tabs and justification conflict with each other: Justification will move content away from its tab-aligned positions. The same is true for alignments other than
Alignment.LEFT.- Parameters:
tabs- aPangoTabArray
-
setText
Sets the text of the layout.This function validates
textand renders invalid UTF-8 with a placeholder glyph.Note that if you have used
setMarkup(java.lang.String, int)orsetMarkupWithAccel(java.lang.String, int, int, org.javagi.base.Out<java.lang.Integer>)on this Layout before, you may want to callsetAttributes(org.gnome.pango.AttrList)to clear the attributes set on the layout from the markup as this function does not clear attributes.- Parameters:
text- the textlength- maximum length oftext,in bytes. -1 indicates that the string is nul-terminated and the length should be calculated. The text will also be truncated on encountering a nul-termination even whenlengthis positive.
-
setWidth
public void setWidth(int width) Sets the width to which the lines of thePangoLayoutshould wrap or get ellipsized.The default value is -1: no width set.
- Parameters:
width- the desired width in Pango units, or -1 to indicate that no wrapping or ellipsization should be performed.
-
setWrap
Sets the wrap mode.The wrap mode only has effect if a width is set on the layout with
setWidth(int). To turn off wrapping, set the width to -1.The default value is
WrapMode.WORD.- Parameters:
wrap- the wrap mode
-
writeToFile
A convenience method to serialize a layout to a file.It is equivalent to calling
serialize(java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutSerializeFlags>)followed byGLib.fileSetContents(java.lang.String, byte[]).See those two functions for details on the arguments.
It is mostly intended for use inside a debugger to quickly dump a layout to a file for later inspection.
- Parameters:
flags-PangoLayoutSerializeFlagsfilename- the file to save it to- Returns:
trueif saving was successful- Throws:
GErrorException- seeGError- Since:
- 1.50
-
writeToFile
A convenience method to serialize a layout to a file.It is equivalent to calling
serialize(java.util.Set<org.gnome.pango.LayoutSerializeFlags>)followed byGLib.fileSetContents(java.lang.String, byte[]).See those two functions for details on the arguments.
It is mostly intended for use inside a debugger to quickly dump a layout to a file for later inspection.
- Parameters:
flags-PangoLayoutSerializeFlagsfilename- the file to save it to- Returns:
trueif saving was successful- Throws:
GErrorException- seeGError- Since:
- 1.50
-
xyToIndex
Converts from X and Y position within a layout to the byte index to the character at that logical position.If the Y position is not inside the layout, the closest position is chosen (the position will be clamped inside the layout). If the X position is not within the layout, then the start or the end of the line is chosen as described for
LayoutLine.xToIndex(int, org.javagi.base.Out<java.lang.Integer>, org.javagi.base.Out<java.lang.Integer>). If either the X or Y positions were not inside the layout, then the function returnsfalse; on an exact hit, it returnstrue.- Parameters:
x- the X offset (in Pango units) from the left edge of the layouty- the Y offset (in Pango units) from the top edge of the layoutindex- location to store calculated byte indextrailing- location to store a integer indicating where in the grapheme the user clicked. It will either be zero, or the number of characters in the grapheme. 0 represents the leading edge of the grapheme.- Returns:
trueif the coordinates were inside text,falseotherwise
-
builder
ALayout.Builderobject constructs aLayoutwith the specified properties. Use the variousset...()methods to set properties, and finish construction withLayout.Builder.build().- Returns:
- the builder object
-